Table of Contents
Physics is a discipline that has helped the world organize nature and the universe. The subject deals with a large number of fundamental concepts occurring naturally. One of the key advantages of studying physics is gaining the ability to see the connections between seemingly disparate phenomena.
Oscillatory motion is one such concept that has revolutionized processes across a wide range of industries. Understanding everything there is to know about this concept can help you appreciate its occurrence in everyday life!
Keep reading to learn more!
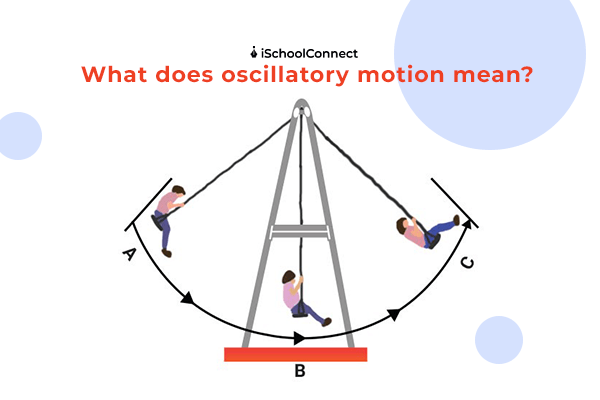
What is oscillatory motion?
Simply put, oscillatory motion is a type of motion that repeats itself. An object oscillates about a fixed equilibrium position due to the presence of torque or restoring force.
The torque or force works to return the system towards its equilibrium position regardless of the direction in which the system has been displaced.
As a concept and application, oscillatory motion plays a significant role in explaining the action of molecules, alternating current circuits, and the behavior of electromagnetic waves.
What are the different types of oscillatory motion?
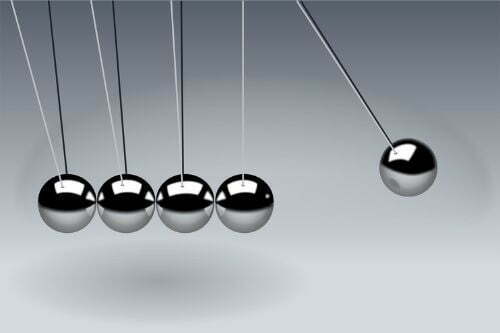
Oscillatory motion is of two types- linear motion and circular motion.
In linear motion, an object moves up and down or left and right. An excellent example of linear motion is the vibration of different strings in a musical instrument or the movement of ships in the sea.
In a circular motion, an object moves left and right but specifically in a circular form. Some of the most popular examples of circular motion include-
- The motion of a pendulum in a watch.
- The motion of a swing on a playground.
The equilibrium position in oscillatory form is the position in which the oscillations occur. In each oscillation, it is a rule that the oscillating object passes through the equilibrium position.
After some time, the motion gradually stops owing to the friction of the medium in which the object is moving. The oscillating object finally comes to rest on the equilibrium.
What are some common examples of oscillatory motion?
Examples are replete throughout nature. Some of the most frequently occurring examples include-
- An oscillation of a simple pendulum.
- The movement of spring.
- Alternating current in electrical equipment.
- A series of oscillations are in the cosmological model.
- The motion of a wheel.
- A stringed object that suspends on a nail.
- The motion of a solid sphere in a half-hollow sphere.
What is simple harmonic motion?
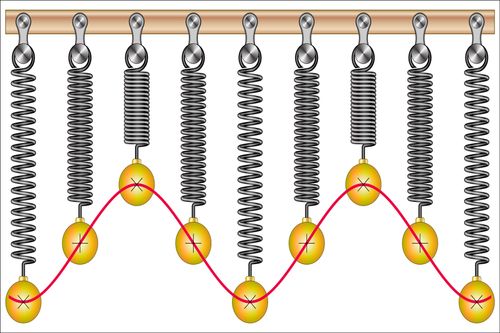
Simple harmonic motion is a type of oscillatory motion. In this motion, the restoring force of the object is directly proportional to the length of its displacement from the equilibrium position. This is referred to as Hooke’s Law.
One of the best ways to explain Hooke’s Law is with the following example-
Imagine a block of mass ‘m’ tied to a long spring. The spring has a spring constant of ‘k’ and one end of it is fixed to a wall. When the block moves horizontally away from the wall, the spring works and tries to restore the position. This is when oscillatory motion begins.
The restoring force that tried to bring back the regular position of the spring is expressed by Hooke’s Law.
The restoring force Fs is described as below-
Fs=-kx
The negative sign demonstrates the force that is acting against the displacement ‘x’.
When the block is displayed from the position, x=A and the restoring force will work to regain its equilibrium. When the block reaches its equilibrium position (x=0), the potential energy is converted to kinetic energy, the kinetic energy pushes the block to another side of the equilibrium point. This is referred to as x=-A.
From this point, the block moves against the right and takes the position of x=A. This is precisely how the oscillatory motion continues until the frictional force begins acting to stop the block. The frictional force is equal to the restoring force.
What is the difference between periodic motion and oscillatory motion?
Periodic motion is a type of motion that repeats itself after fixed periods. This fixed period is known as the time of periodic motion.
On the other hand, oscillatory motion is defined as the to and fro motion of an object around its fixed position. It is a type of periodic motion.
A common example of periodic motion is the motion of hands on a clock or the motion of planets around the sun. Examples of oscillatory motion include the swinging of a pendulum and the vibrating of strings on a musical instrument.
Key takeaways
- As a field, physics has contributed significantly to our understanding of the world around us.
- One such concept that revolutionized different processes around the world is the concept of oscillatory motion.
- Learning everything there is to know about oscillatory motion can help you better understand its applications across different industries.
Was this blog informative? If so, please share your thoughts in the comments below. Click here to reach out to us for more information on the concept of oscillatory motion. We would be happy to assist you with your queries!
Liked this blog? Read next: Concepts of physics that everyone should know of!
FAQs
Q1. What is the unit of frequency?
Answer – The unit of frequency is referred to as Hertz (Hz).
Q2. What is so unique about oscillatory motion?
Answer – The force present in an oscillating system works in the opposite direction as the particle’s movement from an equilibrium point. The restorative force either varies with time or is constant.
Q3. What are the two conditions needed for oscillatory motion?
Answer – The conditions needed for oscillatory motion are ‘inertia’ and ‘stiffness’.