Table of Contents
The study of cells structure and function is known as cell biology, and it is based on the concept that a cell is the basic building block of all life. Research on the tissues and organisms is made possible by concentrating on the cell structure and function.
While some creatures are made up of one cell, others are arranged into massive cooperative groups of many cells. Cell biology as a whole focuses on the structure and function of a cell, from the most universal characteristics shared by all cells to the distinctive and extremely complex functions exclusive to specialized cells.
Definition of study of cell
Cell biology is a branch of biology that focuses on the cell, which is the building block of all living things. It covers all facets of the cell, such as cell structure, cell division (mitosis and meiosis), and cell functions like respiration and cell death. It is a branch of biology that is strongly tied to other branches including genetics, molecular biology, and biochemistry.
Cell research
- The study of cells is based on the cell hypothesis. It is one of the fundamental theories of biology, and would not have been conceivable without the development of the microscope.
- Cell researchers can now obtain precise images of the tiniest cell structures and organelles using cutting-edge microscopes like the scanning electron microscope and transmission electron microscope.
Study of Cells and their types
Cells act as the building blocks of all living things. Certain species have trillions of cells.
Eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells are the two main subtypes of cells. Prokaryotic nuclei are neither well-defined nor membrane-enclosed, in contrast to the nuclei of eukaryotic cells. Even though all organisms are made up of cells, all the cells are not the same.
The composition of organelles and the size, shape, and cell structure are a few of these diverse properties. Animal, bacterial, and plant cells have some similar characteristics, yet they also differ significantly.
Different mechanisms of cell reproduction exist. Binary fission, mitosis, and meiosis are only a few examples of these techniques. DNA, the genetic material that contains the instructions for all cellular functions, is found in an organism’s cells.
Why do cells move?
For many cell processes to take place, cell mobility is required. Cell division, determining cell shape, fending off pathogens, and tissue repair are a few of these processes. Transporting materials in and out of a cell, as well as relocating organelles during cell division, both require internal cell mobility.
Study of Structure of cell

Over time, theories on cell structure have undergone significant changes. Early scientists thought of cells as simple fluid-filled sacs with a few dangling particles. Biologists, today are aware that cells are many times more intricate than this.
The human body contains a wide variety of cell types, sizes, and forms. The idea of a ‘generalized’ cell is introduced for scientific descriptions. All cell types and their functions might differ.
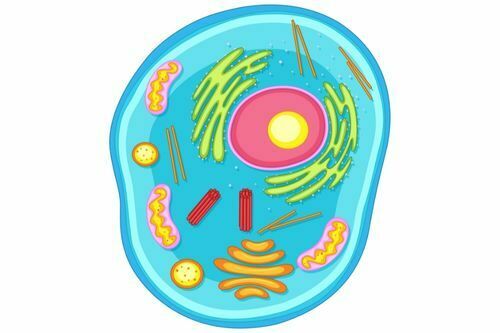
The cell membrane, the nucleus, and the cytoplasm are the three components that make up a cell.
Intricate arrangements of microscopic fibers and hundreds or even thousands of tiny, unique structures known as organelles can be found in the cytoplasm.
Cell membrane
Each cell in the body is enclosed with a cell (plasma) membrane. The cell membrane differentiates between the internal and external components of the cell.
Nucleus and Nucleolus
The control center of the cell is the nucleus, which is made up of a nuclear membrane enclosing fluid nucleoplasm. Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), the cell’s genetic material, is found in chromatin threads in the nucleus.
Cytoplasm
The gel-like substance that fills a cell is called cytoplasm. It catalyzes chemical reactions. It offers a foundation for other organelles to function within the cell.
Cytoplasmic organelles
The ‘little organs’ known as cytoplasmic organelles are suspended within the cytoplasm of the cell. Every type of organelle has a distinct structure and performs a particular function in a cell.
Study of functions of a cells
As you are already aware, a cell is a structural and functional unit of life. Let’s examine some of the most important tasks that a cell performs.
Support and Structure
You know that bricks make up a house. Similar to this, cells make up an organism. Some cells, such as the collenchyma and sclerenchyma, are there to give structural support. All cells generally serve as the foundation for all creatures.
Growth
Simple cell multiplication is how tissues form in complex organisms like humans. As a result, cells are in charge of the organism’s growth. The entire process is carried out through the mitosis process.
Energy Generation
Energy is required by organisms to carry out various chemical processes. The process of photosynthesis provides energy to plants, whereas respiration provides energy to animals.
Metabolism
The metabolism of an organism, which comprises all the internal chemical processes necessary to maintain life is controlled by the cell.
Key takeaways
- Cell biology is the study of how cells work and how they are made, and it is centered on the idea that cells are the fundamental unit of life. By focusing on cell structure and function, research on tissues and organisms is made possible.
- There are many different cell kinds, sizes, and shapes in the human body. Scientific descriptions introduce the concept of a ‘generalized’ cell. Different cell types have different functions.
- Cells are a structural and functional unit of life and they perform different functions. They are responsible for support and structure, metabolism, and growth.
Did you find this blog informative? If so, please share your thoughts in the comments section below. Click here to contact us for more information on the study of cells. We would be happy to assist you with your queries.
Liked this blog? Read next: BSc Microbiology Subjects | All You Need to Know
FAQs
Q1. Which biologist studies cells?
Ans- Cellular biologists examine and research the physiological makeup of cells and how they interact with other living things.
Q2. Which is the smallest cell?
Ans-Mycoplasma or PPLO (Pleuropneumonia like organism) is the smallest cell.
Q3. How many cells does a human body have?
Ans- According to recent studies, the average human body consists of 30 trillion cells.







